NOTE: Homebrew has been dubbed “The Missing Package Manager for OS X”. With Homebrew, you can install any command utility in just a few keystrokes and update them all with just a few more.
- Mac Install App Via Terminal Number
- Mac Terminal Program
- Mac Install App Via Terminal Linux
- Terminal For Mac
Homebrew will enable many terminal commands that Linux users will find familiar, in fact, most of the commands are exactly the same as what is included “out-of-the-box” with many Linux distros.
Tutorial – Install applications via Terminal+homebrew (MAC) NOTE: Homebrew has been dubbed “The Missing Package Manager for OS X”. With Homebrew, you can install any command utility in just a few keystrokes and update them all with just a few more.
- Copy the Install macOS Mojave.app installer file to the target computers /Applications folder. Enter or deploy the following command to the target system(s).
- Open up Terminal (Applications Utilities) and type in: sudo find / -iname.app. This will display all the apps you have on your computer. From there, you can copy and paste the results into a.
Below, you will find a step-by-step guide to installing applications via Terminal + Homebrew.
1) To install Homebrew, open a terminal window and copy/paste the following command, then hit enter:
ruby -e “$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)”
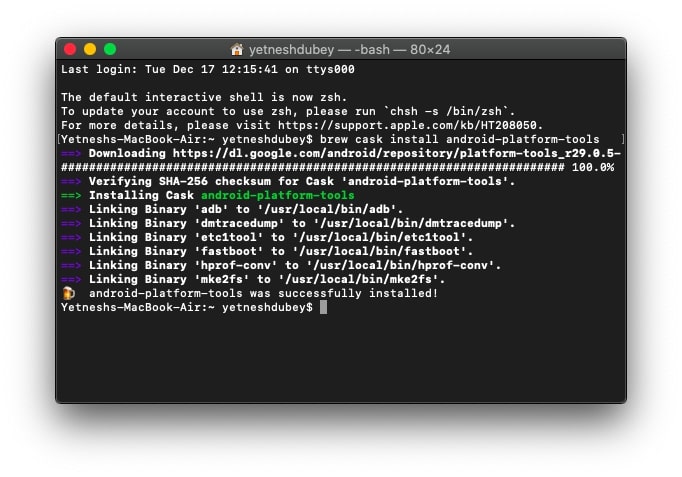
2) Copy/paste the following command to install wget (package retriever for terminal):
brew install wget
3) Copy/Paste the folling command to install Cask (desktop application installer for terminal):
brew install caskroom/cask/brew-cask
Mac Install App Via Terminal Number

If all goes well, you should now be able to install packages as well as desktop apps via terminal on your mac.
For a full list of Homebrew commands for installing packages/apps, visit brewformulas.org
Use kickstart to set Apple Remote Desktop preferences. For example, you can install, uninstall, activate, set up, and restart Apple Remote Desktop components.
Learn how to control a remote Mac with Screen Sharing with the kickstart command-line utility in macOS Mojave 10.14 and later.
Get started
You can find the kickstart tool at:
/System/Library/CoreServices/RemoteManagement/ARDAgent.app/Contents/Resources/kickstart
Type the commands in this article as one line of text. If the text wraps as you enter it, that's fine. Don’t press the Return key until you’ve entered the entire command.
For more information about the kickstart command, use the -help flag:
Mac Terminal Program
Sample commands
Mac Install App Via Terminal Linux
The commands in this article work with Apple Remote Desktop 3.2 and later.
Here are commands that you can use:
Terminal For Mac
- Restart the ARD Agent and helper:
- Turn on Remote Desktop Sharing, allow access for all users, and enable the menu extra:
- Turn on Remote Desktop Sharing, allow access for specified users:
You must use the -configure, -access, and -privs options in a separate command to specify the set of users and their access privileges. For example, this command is for users with the short names 'teacher' and “student.' It gives them access to observe (but not control) the computer, and to send text messages:
Unlike other kickstart options, you can’t combine the allowAccessFor options with other kickstart options. You must use it as in the last two samples above. You might have to call kickstart more than once to finish a computer’s setup. - Remove access privileges for specified users ('student' in this example):
- Disable ARD Agent and remove access privileges for all users: